EMPLOYER || CANDIDATE
EMPLOYER || CANDIDATE
HR Planning
Employer
Strategic Human Resource Planning
Strategic Human Resources planning is an important component of strategic HR management.
It links HR management directly to the strategic plan of your organization. Most mid- to large sized organizations have a strategic plan that guides them in successfully meeting their missions.
Organizations routinely complete financial plans to ensure they achieve organizational goals and while workforce plans are not as common, they are just as important.
Even a small organization with as few as 10 staff can develop a strategic plan to guide decisions about the future. Based on the strategic plan, your organization can develop a strategic Human Resources plan that will allow you to make HR management decisions now to support the future direction of the organization.
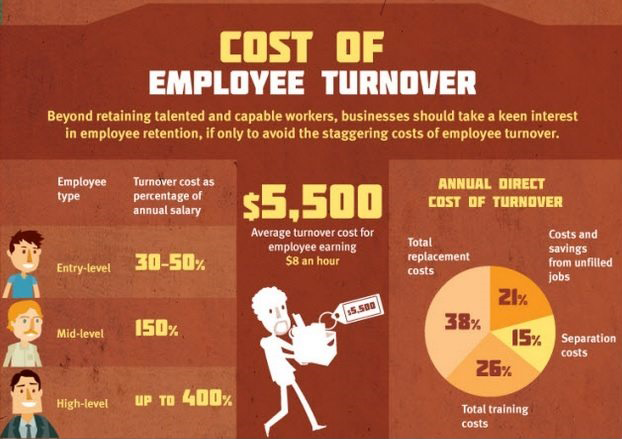
Strategic HR planning is also important from a budgetary point of view so that you can factor the costs of retention, turnover, recruitment, OnBoarding and training, etc. into your organization's operating budget.
Integrating human resource management strategies and systems to achieve the overall mission, strategies, and success of the firm while meeting the needs of employees and other stakeholders.
Introduction to Strategic Human Resources Planning
The overall purpose of strategic HR planning is to:
Ensure adequate human resources to meet the strategic goals and operational plans of your organization - the right people with the right skills at the right time
Keep up with social, economic, legislative and technological trends that impact on human resources in your area and in the sector
Remain flexible so that your organization can manage change if the future is different than anticipated
Strategic HR planning predicts the future HR management needs of the organization after analyzing the organization's current human resources, the external labour market and the future HR environment that the organization will be operating in.
The analysis of HR management issues external to the organization and developing scenarios about the future are what distinguishes strategic planning from operational planning.
SILICON STAFFING
CAN FILL THE HR ROLE FOR YOUR COMPANY
The basic questions to be answered for strategic planning are:
Where are we going?
How will we develop HR strategies to successfully get there, given the circumstances?
What skill sets do we need?
The Strategic HR Planning Process
Assessing the current HR capacity
Forecasting HR requirements
Gap analysis
Developing HR strategies to support organizational strategies
Based on the organization's strategic plan, the first step in the strategic HR planning process is to assess the current HR capacity of the organization. The knowledge, skills and abilities of your current staff need to be identified. This can be done by developing a skills inventory for each employee.
The skills inventory should go beyond the skills needed for the particular position. List all skills each employee has demonstrated. For example, recreational or volunteer activities may involve special skills that could be relevant to the organization.
Education levels and certificates or additional training should also be included. An employee's performance assessment form can be reviewed to determine if the person is ready and willing to take on more responsibility and to look at the employee's current development plans
.
The next step is to forecast HR needs for the future based on the strategic goals of the organization. Realistic forecasting of human resources involves estimating both demand and supply.
Questions to be answered include:
How many staff will be required to achieve the strategic goals of the organization?
What jobs will need to be filled?
What skill sets will people need?
When forecasting demands for HR, you must also assess the challenges that you will have in meeting your staffing need based on the external environment.
To determine external impacts, you may want to consider some of the following factors:
How does the current economy affect our work and our ability to attract new employees?
How do current technological or cultural shifts impact the way we work and the skilled labor we require?
What changes are occurring in the Canadian labor market?
How is our community changing or expected to change in the near future?
The next step is to determine the gap between where your organization wants to be in the future and where you are now. The gap analysis includes identifying the number of staff and the skills and abilities required in the future in comparison to the current situation.
You should also look at all your organization's HR management practices to identify practices that could be improved or new practices needed to support the organization's capacity to move forward. Questions to be answered include:
What new jobs will we need?
What new skills will be required?
Do our present employees have the required skills?
Are employees currently in positions that use their strengths?
Do we have enough managers/supervisors?
Are current HR management practices adequate for future needs?

There are five HR strategies for meeting your organization's needs in the future:
Restructuring strategies
Training and development strategies
Recruitment strategies
Outsourcing strategies
Collaboration strategies
Restructuring Strategies
This strategy includes:
Reducing staff either by termination or attrition
Regrouping tasks to create well designed jobs
Reorganizing work units to be more efficient
If your assessment indicates that there is an oversupply of skills, there are a variety of options open to assist in the adjustment. Termination of workers gives immediate results.
Generally, there will be costs associated with this approach depending on your employment agreements. Notice periods are guaranteed in all provinces.
Be sure to review the employment and labor standards in your province or territory to ensure that you are compliant with the legislation.
Documenting the Strategic HR Plan
Implementing the Strategic HR Plan
Agreement with the Plan
Ensure that the board chair, executive director and senior managers agree with the strategic HR plan. It may seem like a redundant step if everyone has been involved all the way along, but it's always good to get final confirmation.
Communication
The strategic HR plan needs to be communicated throughout the organization.
Your communication should include:
How the plan ties to the organization's overall strategic plan
What changes in HR management policies, practices and activities will be made to support the strategic plan
How any changes in HR management will impact on staff including a time frame if appropriate
How each individual member of staff can contribute to the plan
How staff will be supported through any changes
How the organization will be different in the future
It is impossible to communicate too much (but all too easy to communicate too little), specially when changes involve people. However, the amount of detail should vary depending upon the audience.
Legislation and mandate
Ensure that the actions you are considering are compliant with existing laws, regulations and the constitution and bylaws of your organization.
To review laws relating to employment, visit the HR Toolkit section on Employment Legislation and Standards
Organizational Needs
Whether you are increasing or reducing the number of employees, there are implications for space and equipment, and on existing resources such as payroll and benefit plans.
Evaluation
HR plans need to be updated on a regular basis. You will need to establish the information necessary to evaluate the success of the new plan. Benchmarks need to be selected and measured over time to determine if the plan is successful in achieving the desired objectives.